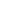Common Symptoms of a Faulty Suction Control Valve
The Suction Control Valve (SCV) is a crucial component in HVAC systems, regulating refrigerant flow and pressure to maintain optimal performance. It ensures precise control of refrigerant circulation, preventing over- or under-supply that can affect efficiency. A malfunctioning SCV can lead to inconsistent airflow, reduced cooling or heating capacity, and increased energy consumption.
What Is a Suction Control Valve?
A suction control valve regulates refrigerant flow and pressure in an HVAC system. Located within the compressor, it adjusts suction levels to maintain optimal system performance.
Key benefits of a well-functioning SCV include:
- Precise Refrigerant Flow: Ensures the right amount of refrigerant circulates for efficient cooling or heating.
- Optimised Performance: Maintains system efficiency by preventing over- or under-supply of refrigerant.
- System Protection: Reduces strain on the compressor, extending the lifespan of HVAC components.
Suction Control Valve Symptoms
Identifying suction control valve issues early can prevent costly HVAC system failures. Common signs include:
- Irregular Airflow: Fluctuating air distribution due to inconsistent pressure regulation.
- System Short Cycling: Frequent on-and-off cycling caused by improper refrigerant flow.
- Higher Energy Consumption: Increased power usage due to inefficient system operation.
- Unexpected Shutdowns: Sudden system failure linked to pressure imbalances.
- Reduced Cooling or Heating Efficiency: Limited performance as the system compensates for valve malfunctions.
Identifying suction control valve issues early can prevent costly HVAC failures. Common signs include irregular airflow, frequent short cycling, higher energy consumption, unexpected shutdowns, and reduced cooling or heating efficiency. Addressing these issues promptly helps maintain optimal system performance.
Root Causes of Suction Control Valve Failures
Suction control valve failures in HVAC systems often result from:
- Wear and Tear: Continuous operation leads to gradual deterioration, reducing efficiency over time.
- Contaminated Refrigerant: Moisture, debris, or impurities in the refrigerant can clog or damage the valve.
- Electrical Issues: Faulty wiring, damaged connectors, or irregular voltage supply can cause erratic valve performance.
- Poor Maintenance: Lack of regular inspections and servicing allows minor issues to worsen, leading to system inefficiencies or failures.
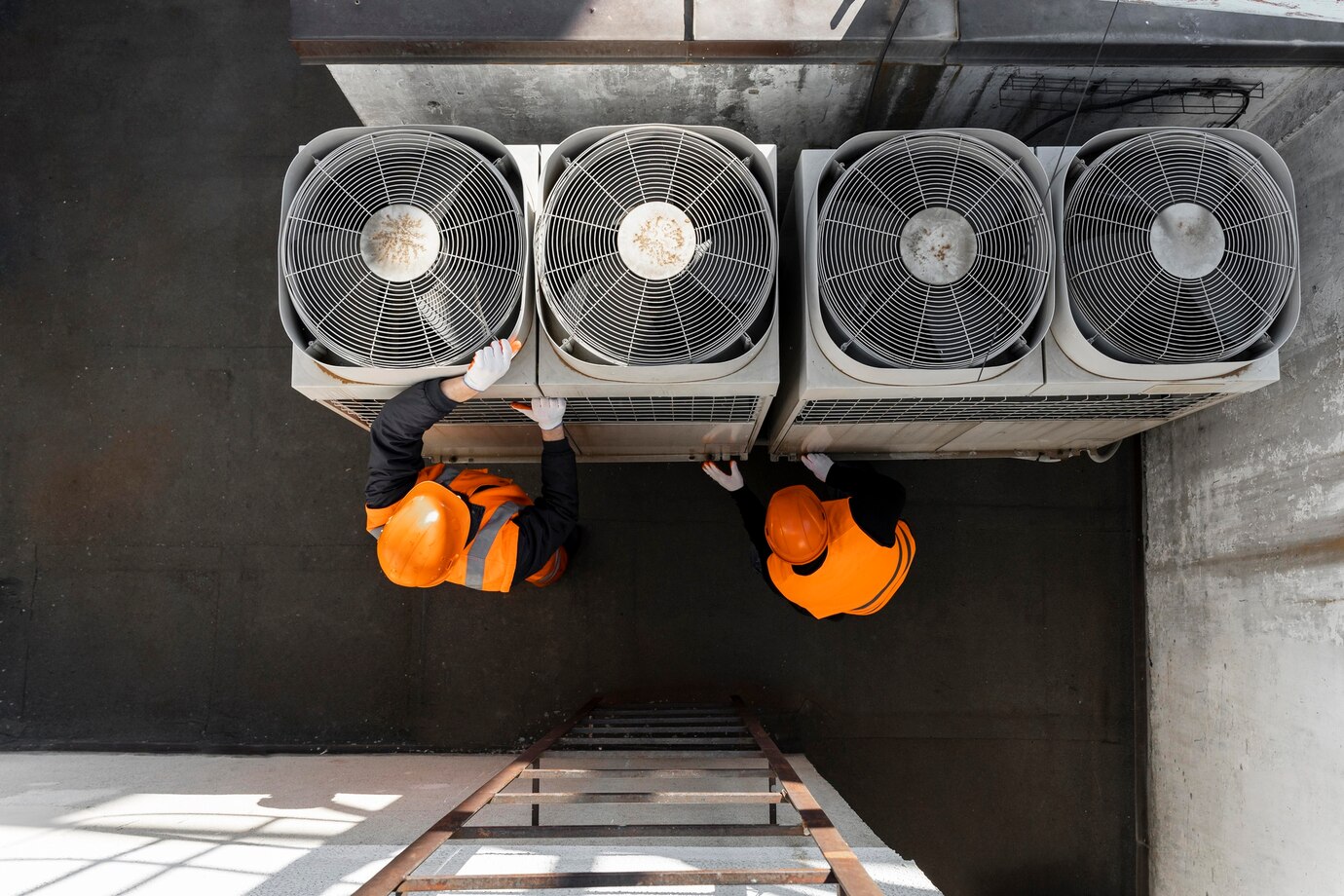

How to Test a Suction Control Valve
To test a suction control valve, follow these steps:
- Inspect the SCV:
- Check for visible damage or debris on the valve.
- Use a Diagnostic Tool:
- Scan the ECU for fault codes that indicate a malfunctioning SCV.
- Measure Resistance:
- Use a multimeter to test the SCV's connector and confirm it meets standard specifications.
- Pressure Test:
- Monitor fuel rail pressure while the engine runs to check if the SCV adjusts the flow correctly.
Maintenance Tips for Suction Control Valves
Suction control valve failures in HVAC systems often result from:
- Wear and Tear: Continuous operation leads to gradual deterioration, reducing efficiency over time.
- Contaminated Refrigerant: Moisture, debris, or impurities in the refrigerant can clog or damage the valve.
- Electrical Issues: Faulty wiring, damaged connectors, or irregular voltage supply can cause erratic valve performance.
- Poor Maintenance: Lack of regular inspections and servicing allows minor issues to worsen, leading to system inefficiencies or failures.
A new SCV installed with these precautions ensures reliable fuel pump operations and optimal engine performance.
When to Seek Professional Help
Consult a professional if you notice persistent suction control valve symptoms such as rough idling or poor acceleration on your HVAC.
Conclusion
Regular maintenance, using high-quality refrigerant, and monitoring suction control valves are essential for optimal HVAC system performance. Addressing issues early helps prevent costly repairs and system failures. Persistent symptoms should be diagnosed by an HVAC professional, with replacement considered if necessary.
If you’re experiencing suction control valve issues or need a reliable replacement, explore high-quality SCV options and expert assistance at Controls Traders. Keep your HVAC system running efficiently with trusted solutions tailored to your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common symptoms of a faulty suction control valve?
A faulty suction control valve in an HVAC system can cause inconsistent airflow, frequent short cycling, higher energy consumption, unexpected shutdowns, and reduced cooling or heating efficiency. If these issues persist, professional inspection and possible replacement may be needed.
How can I test my suction control valve?
To test your suction control valve in an HVAC system, monitor pressure readings for irregularities, listen for unusual noises, and check for inconsistent airflow. If issues persist, a professional technician can perform diagnostic tests and calibrate or replace the valve if necessary.
What causes a suction control valve to fail?
A suction control valve in an HVAC system can fail due to wear and tear, refrigerant contamination, electrical issues, or lack of regular maintenance. These factors can lead to improper refrigerant flow, reduced efficiency, and system malfunctions.
Is it possible to repair a suction control valve, or should it be replaced?
A suction control valve in an HVAC system is typically replaced rather than repaired as internal components wear out or become contaminated over time. If the valve is malfunctioning, a professional technician can assess whether cleaning or calibration is possible, but replacement is often the most effective solution.
When should I seek professional help for a faulty suction control valve?
A suction control valve in an HVAC system is usually replaced rather than repaired, as wear, contamination, or electrical issues can affect its performance. Seek professional help if you notice inconsistent airflow, short cycling, high energy consumption, or system shutdowns to prevent further damage.
Leave a comment
Popular Posts

Voltage Converters: Learn How They Work and How to Pick the Best Type

What is a Variable Speed Drive? A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding VSDs

What is a VFD in HVAC and How Does it Work?